Each year, around 7,500 women in the UK are diagnosed with ovarian cancer, primarily over the age of 50. Most of them are over 50. It’s very important to spot the warning signs early to get the right treatment. Many women ask: What is the biggest symptom of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer often shows up with small symptoms. These include bloating, constant pain in the belly or pelvis, feeling full fast after eating, and needing to pee a lot. These signs are easy to miss. So, knowing the first symptom is key to catching it early.
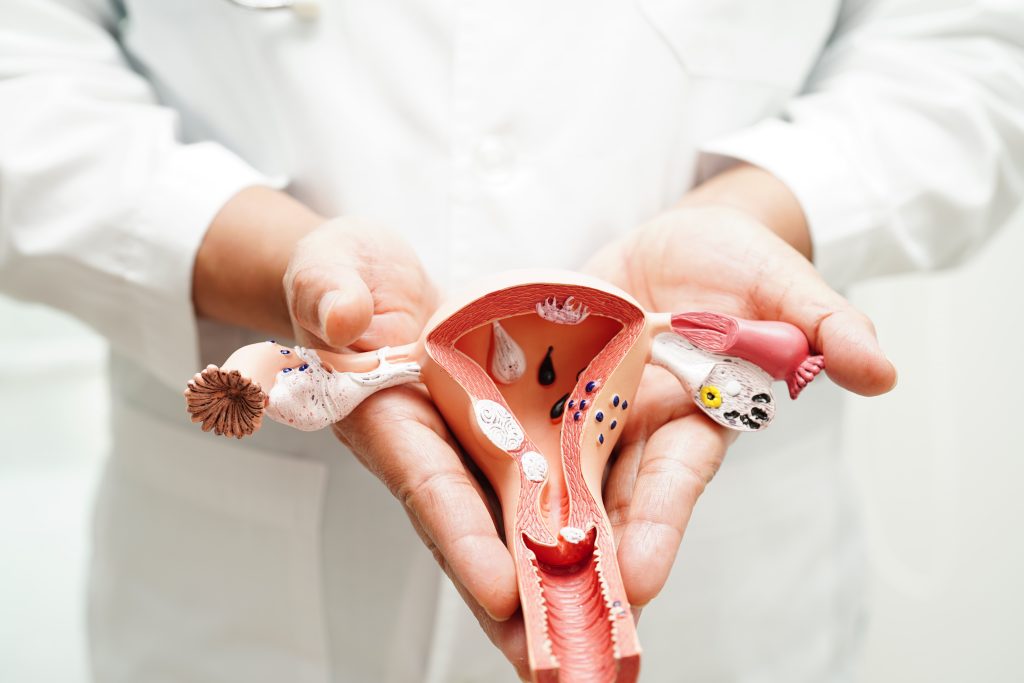
It’s important to know about ovarian cancer to catch it early and treat it well. This disease grows in the ovaries and can cause serious health problems if not treated quickly.
Ovarian cancer is divided into several types based on where it starts. The main types are:
Each type has its own signs and symptoms. Knowing these differences is key for a correct diagnosis.
Ovarian cancer is a big health issue in the U.S., with many new cases every year. It’s one of the top five cancer killers in women. It’s often found late because its symptoms are not clear.
The American Cancer Society shares important facts about ovarian cancer. This includes how common it is, survival rates, and death numbers. Knowing these stats helps raise awareness and push for early detection.
Ovarian cancer is often called the ‘silent killer’ because it can grow without being noticed until it’s too late. This makes finding it early both important and hard.
In its early stages, ovarian cancer usually doesn’t show symptoms or shows symptoms that seem minor. This makes it hard for women to know they have it and for doctors to catch it early. A new blood test might help by finding two specific markers in people with symptoms like pelvic pain and bloating. This new test could change how we find ovarian cancer.
“The lack of specific symptoms in early-stage ovarian cancer contributes to its ‘silent killer’ reputation.”
Spotting ovarian cancer symptoms early is key to saving lives. Even though it’s often found late, knowing the early signs can lead to quicker diagnosis and better treatment. Signs include constant bloating, pelvic or stomach pain, trouble eating, and needing to pee a lot.
| Symptom | Description |
| Persistent Abdominal Bloating | A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdominal area that persists over time. |
| Pelvic or Abdominal Pain | Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region or abdomen. |
| Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly | Feeling unusually full after eating small amounts of food. |
| Urinary Frequency or Urgency | Needing to urinate more often than usual or feeling a sudden, urgent need to urinate. |
It’s important for both patients and doctors to know these symptoms. Spotting them early can lead to better treatment and outcomes for ovarian cancer patients.
Persistent abdominal bloating is often seen as the biggest symptom of ovarian cancer. Yet, it’s often overlooked or misunderstood. This symptom can be a subtle yet critical indicator of the disease’s presence.
Cancer-related bloating in ovarian cancer shows as a persistent swelling of the abdomen. Unlike normal bloating, which comes and goes, this type gets worse over time. It can also feel tight and uncomfortable.
The key characteristic of cancer-related bloating is its persistence. While occasional bloating is common and usually harmless, persistent bloating lasting more than a few weeks should be checked by a healthcare professional.
It can be hard to tell normal bloating from pathological bloating. Normal bloating is often due to diet, hormones, or gut issues. Pathological bloating, linked to ovarian cancer, is more persistent and may come with other symptoms like pelvic pain or trouble eating.
Knowing these differences can help people recognize when their symptoms need further check-ups.
Bloating is a common symptom with many causes, most of which are not serious. So, it’s often seen as a minor issue, like bad diet, irritable bowel syndrome, or hormonal changes.
The challenge is to tell apart harmless bloating from bloating that might mean ovarian cancer. Doctors must carefully look at persistent bloating, and other symptoms, to find the real cause.
By knowing about cancer-related bloating and watching for persistent symptoms, people can get medical help early. This can lead to better outcomes.
Ovarian cancer shows signs beyond just persistent bloating. It’s important to know these cancer common symptoms for early treatment.
Pelvic or abdominal pain is a common cancer initial symptom. This pain can feel like a dull ache or sharp pains. It doesn’t go away with usual pain relief.
This pain happens when the tumor presses on nearby areas or causes inflammation.
Women with ovarian cancer often have trouble eating or feel full fast. This can cause weight loss and malnutrition. The cancer affects the digestive system or presses on the stomach.
Ovarian cancer can also lead to urinary issues like needing to pee a lot or urgently. The tumor can press on the bladder or nerves, causing these problems.
Back pain is another symptom of ovarian cancer. It happens when the tumor presses on nerves or structures in the back. This pain can get worse if not treated.
Knowing these symptoms and their link to ovarian cancer is key. If you have any of these common cancer symptoms, see a doctor for a check-up and diagnosis.
Spotting the first signs of ovarian cancer early can make a big difference. Ovarian cancer is called a “silent killer” because its symptoms are often mild and can be mistaken for other issues.
Ovarian cancer symptoms can take months to show up. At first, they might be mild and not last long, making it hard to catch the disease early.
Early symptoms can feel like just not feeling well. It’s key to notice any ongoing changes in your body.
As ovarian cancer gets worse, symptoms don’t go away and get stronger. You might feel more abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, or have trouble eating because you feel full too fast.
If you keep feeling symptoms that don’t feel right, see a doctor. A blood test can find ovarian cancer early and accurately, showing why it’s important to act fast.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Abdominal Bloating | Feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen | Consult a doctor if persistent |
| Pelvic Pain | Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area | Seek medical attention if severe or persistent |
| Difficulty Eating | Feeling full quickly or loss of appetite | Discuss with a healthcare provider |
Ovarian cancer can show symptoms beyond the usual ones. Abdominal bloating is well-known, but other signs can also point to ovarian cancer. Knowing these symptoms is key for early detection and treatment.
Fatigue is a common symptom of ovarian cancer. It’s feeling tired all the time, even after resting. This symptom can be tricky because it’s seen in many other conditions too.
Unexplained weight changes, like gaining or losing weight, are also important. These changes happen because of the body’s reaction to cancer. It’s important to watch for these changes and understand why they happen.
Changes in bowel habits, like constipation or diarrhea, can be signs of ovarian cancer. These changes might happen because of the tumor’s pressure or other metabolic changes. Spotting these changes early can help with diagnosis.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, like irregular periods or bleeding after menopause, is a symptom to watch. While it’s often linked to other gynecological issues, it could also mean ovarian cancer if seen with other symptoms.
It’s important to know about these less common symptoms and talk to a healthcare provider if you have concerns. Catching ovarian cancer early can greatly improve treatment options.
Ovarian cancer symptoms can change a lot based on the type and stage. Knowing these differences is key for catching it early and treating it well.
In the early stages, ovarian cancer might show mild or vague symptoms. These can be easy to miss. Common signs include persistent abdominal bloating and pelvic pain.
As the cancer gets worse, symptoms get more serious. You might feel severe abdominal pain, significant weight loss, or difficulty eating or feeling full quickly.
The cancer’s growth from early to late stages means symptoms get worse. Spotting the cancer primary symptom early can really help with treatment.
Ovarian cancer is divided into types based on where it starts. Epithelial ovarian cancer, the most common, often shows as abdominal bloating and pelvic pain. Germ cell tumors are more common in younger women and can cause abdominal pain and pelvic masses.
Stromal cell tumors can make hormones, leading to symptoms like endometrial hyperplasia or virilization.
Each type of ovarian cancer has its own set of symptoms. It’s important to know the specific cancer common symptom profiles for accurate diagnosis.
Borderline ovarian tumors are less likely to be cancerous than invasive ones. Symptoms can be similar to early-stage ovarian cancer, like pelvic pain and abdominal bloating. Catching borderline tumors early is key for managing them well and keeping fertility options open.
Understanding the differences in ovarian cancer symptoms by type and stage can greatly improve early detection and treatment. Knowing the cancer primary symptom and the specific symptoms of different types is vital for managing the disease.
Ovarian cancer symptoms can be mistaken for other, less serious conditions. This makes it hard to catch it early. Both patients and doctors might think these symptoms are from more common issues.
Symptoms like bloating, stomach pain, and trouble eating are seen in ovarian cancer. They can also point to issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastritis, or constipation. This similarity can cause delays in finding the right diagnosis.
| Symptom | Ovarian Cancer | Gastrointestinal Disorders |
| Bloating | Common due to tumor growth | Common in IBS and other GI issues |
| Abdominal Pain | Can be due to tumor pressing on other organs | Often related to digestive issues |
Feeling the need to pee a lot or urgently can be a sign of ovarian cancer. But, it’s also a symptom of urinary tract infections (UTIs) or other urological problems. Women with these symptoms might first be treated for UTIs or overactive bladder, without thinking of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms like pelvic pain and unusual vaginal bleeding can be signs of ovarian cancer. But, they’re also seen in conditions like endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or menstrual issues. It’s important to make a precise diagnosis to tell these conditions apart.
It’s key to know how ovarian cancer symptoms can be mixed up with other issues. Doctors need to be careful and think of ovarian cancer when they see these symptoms. This helps in getting the right diagnosis on time.
Knowing the risk factors for ovarian cancer is key for early detection. Some factors can raise a woman’s chance of getting ovarian cancer. It’s vital to know the cancer main symptom and other warning signs.
Several risk factors can increase the chance of ovarian cancer. These include genetic predispositions, family history, and age.
Women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations face a higher risk of ovarian cancer. These genetic changes are linked to a family history of breast and ovarian cancer. Knowing about these mutations can help women stay alert to their health and spot the cancer warning sign.
A family history of ovarian, breast, or related cancers raises a woman’s risk. Cancers in first-degree relatives, like a mother or sister, are a big concern. Women with a strong family history should watch their health closely and talk to their doctor about their risk.
Ovarian cancer mostly affects women over 50. Obesity, reproductive history, and certain fertility treatments can also affect risk. Knowing these demographic factors can help women understand their risk better.
The following table summarizes the key risk factors and their implications for ovarian cancer awareness:
| Risk Factor | Description | Implication |
| Genetic Mutations (BRCA1/BRCA2) | Mutations in these genes increase ovarian cancer risk. | Proactive monitoring and awareness of cancer symptoms. |
| Family History | History of ovarian, breast, or related cancers in close relatives. | Increased vigilance and discussion with healthcare providers. |
| Age | Risk increases significantly after age 50. | Regular check-ups and awareness of cancer warning signs. |
By understanding these risk factors, women can better recognize the importance of being aware of ovarian cancer symptoms. They can take the right steps to manage their health.
When symptoms of ovarian cancer show up, patients start a detailed diagnostic process. This is key to find out what’s causing the symptoms and what to do next.
The first step is a visit to the doctor. Here, a full medical history is taken and a physical exam is done. The doctor will ask about the key symptoms, how long they’ve lasted, and what makes them better or worse.
A pelvic exam is also part of this first check. It helps the doctor look for any unusual changes in the reproductive organs.
Blood tests play a big role in diagnosis. One test checks the CA-125 biomarker in the blood. High CA-125 levels might mean ovarian cancer, but it’s not the only cause. It’s important to know that not all ovarian cancers show up in CA-125 tests, and other issues can also cause high levels.
Imaging tests help see the ovaries and nearby areas. An ultrasound is often the first test, as it can spot problems like cysts or tumors. More tests like CT scans or MRI might be needed to see how far the disease has spread and plan treatment.
Often, surgery is needed to confirm ovarian cancer. This involves taking out the tumor or affected ovary and nearby tissues for a closer look. During surgery, doctors check how far the cancer has spread. This is important for figuring out the cancer’s stage. The stage helps predict how the cancer will do and what treatment is best.
The steps to diagnose ovarian cancer are complex. Knowing about these steps can help patients better understand their journey through diagnosis.
Spotting the first signs of ovarian cancer is more than a medical issue. It’s also an emotional challenge. When women notice possible symptoms, they often feel anxious and fearful. These feelings can affect their mental health and daily life.
When a woman notices a cancer primary symptom, she may feel very anxious. This anxiety comes from not knowing what’s happening and the fear of a cancer diagnosis.
These feelings can show up in many ways. Women might worry a lot, have trouble sleeping, or avoid going to the doctor. It’s important for them to talk about these feelings with healthcare providers, family, and friends.
Going through diagnostic tests can be stressful. But, there are ways to handle this stress. Staying informed about what’s happening can help. Women can also find support in support groups where they can share and learn from others.
Using mindfulness and relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing can also help. Talking openly with healthcare providers about fears and concerns is key for emotional support.
By understanding the emotional impact of recognizing symptoms and using effective coping strategies, women can manage the diagnostic process better. This prepares them for what comes next, whether it’s more tests or treatment.
When you get an ovarian cancer diagnosis, knowing your treatment options is key. The right treatment depends on the cancer stage, your health, and what you prefer.
Surgery is a big part of treating ovarian cancer. It aims to remove as much tumor as possible and figure out how far the cancer has spread. Debulking surgery tries to leave as little cancer behind as possible. This can make other treatments work better.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s often used after surgery to get rid of any cancer left behind. The type of chemotherapy depends on the cancer’s stage and type.
Targeted therapies aim to kill cancer cells without harming healthy ones. PARP inhibitors are used for ovarian cancer, mainly in those with BRCA mutations. New treatments like immunotherapy are being tested in trials.
The way we treat ovarian cancer is always getting better. Research is focused on better results and fewer side effects. Talk to your doctor to find the best treatment for you.
For those with ovarian cancer, managing symptoms is key. The cancer major symptom that often stays is abdominal bloating. It can be upsetting and affect daily life.
During treatment, patients face many symptoms. These include pelvic or abdominal pain and difficulty eating or feeling full quickly. It’s important to manage these symptoms well to keep patients comfortable and on track with treatment.
Doctors may suggest different ways to handle these symptoms. This could be through pain meds, changing what you eat, or other specific plans for each person.
Survivors of ovarian cancer may face long-term symptoms. These include cancer key symptom like fatigue or changes in bowel habits. It’s important to know about these effects to give full care.
Follow-up care should watch for these symptoms and deal with them quickly. This helps improve the survivor’s life quality.
| Symptom | Management Strategy |
| Fatigue | Conservation of energy, rest, and physical activity tailored to the individual’s capacity |
| Changes in Bowel Habits | Dietary modifications, medication, or other interventions as needed |
By focusing on both immediate and long-term symptom management, healthcare providers can greatly improve care and life quality for those with ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer can’t be fully prevented, but some steps can lower the risk. Knowing these steps is key, mainly for those at higher risk.
Several lifestyle choices can help lower ovarian cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy weight is one, as obesity increases cancer risk. Eating a balanced diet with fruits, veggies, and whole grains also helps.
Regular exercise is another key factor. Exercise keeps weight in check and has its own cancer-fighting benefits. Aim for moderate-intensity workouts often.
Those at high risk, like BRCA1 or BRCA2 carriers, should take extra steps. Genetic counseling helps understand personal risk and discuss ways to lower it.
Some may choose prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy, removing ovaries and fallopian tubes. This choice is big and should be made with healthcare advice.
Oral contraceptives can lower ovarian cancer risk. The longer you use them, the more protection you get, even after stopping.
But, oral contraceptives aren’t right for everyone. Talk to a doctor about the pros and cons based on your health and risks.
Knowing the biggest symptom of ovarian cancer is key for early detection and treatment. Signs like persistent bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, trouble eating, and frequent urination are important. They should not be ignored.
Spotting these symptoms early can greatly improve treatment results. Being aware of these signs can help people get medical help quickly. This could lead to better treatment outcomes.
It’s important to know the symptoms and risk factors of ovarian cancer. This knowledge helps individuals take care of their health. It also allows doctors to make accurate and timely diagnoses.
The biggest symptom of ovarian cancer is persistent abdominal bloating. It often comes with other symptoms like pelvic or abdominal pain. You might also feel full quickly, have to go to the bathroom a lot, or experience back pain.
Main symptoms include persistent bloating and pain in the pelvic or abdomen. You might also feel full quickly, need to go to the bathroom often, or have back pain. Other signs are fatigue, unexplained weight changes, changes in bowel habits, and abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Ovarian cancer-related bloating is a persistent and growing swelling in the abdomen. It’s often accompanied by discomfort or pain. Unlike normal bloating, it gets worse over time.
Risk factors include genetic predispositions like BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations. Family history of ovarian or breast cancer, age, and demographic factors also play a role. Women with a history of endometriosis or infertility are at higher risk.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, blood tests (like CA-125 biomarker), and imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI). Surgical diagnosis and staging are also used.
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and new treatments. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage and type, and the patient’s health.
While prevention is not guaranteed, lifestyle choices can help. Using oral contraceptives, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding toxins are good steps.
Early symptoms are often mild. They might include pelvic or abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all.
Symptoms vary by type and stage. Early-stage cancer might have mild or no symptoms. Late-stage cancer has more severe and persistent symptoms.
Recognizing symptoms can cause a lot of anxiety and fear. It’s important to seek medical help if symptoms don’t go away. Coping strategies are also key during the diagnostic process.
Managing symptoms requires a full approach. This includes managing symptoms during treatment, considering long-term symptoms, and survivorship care.
Have questions or need assistance? Our team is here to help you with appointments, services, or general inquiries.